This article explores THCV, a CB1 antagonist, and its potential role in weight loss. We’ll also examine THCV’s relationship with insulin resistance. Finally, we’ll explore how THCV affects appetite. A 2009 study suggests that THCV could reduce appetite by blocking the CB1 receptor, which is known to stimulate hunger. But more research is needed before THCV can be recommended for human use.
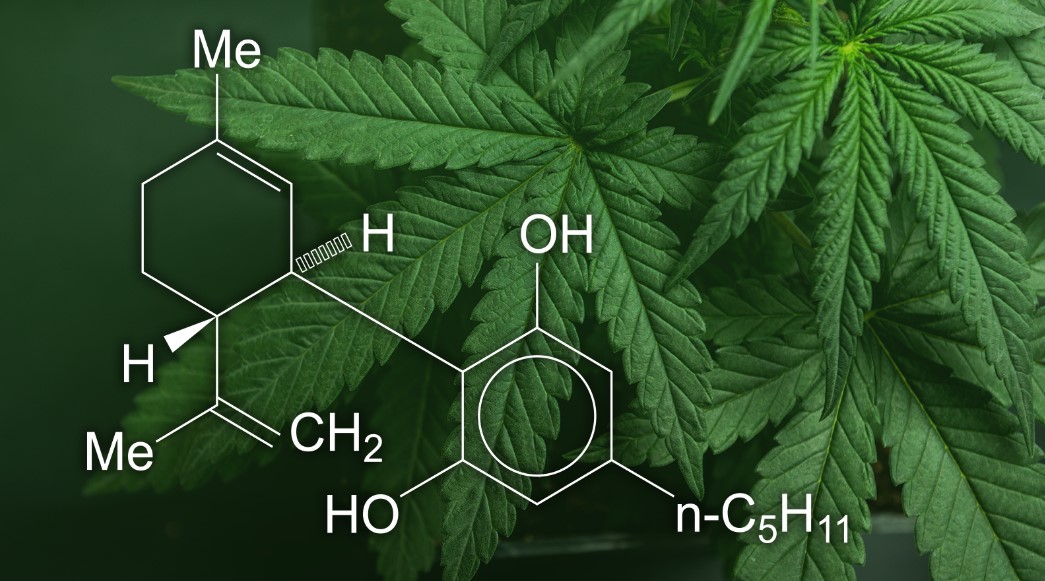
THCV
THCV is a natural analog of THC, a psychoactive cannabinoid. Like THC, it binds to the CB1 receptor but has opposite effects. Depending on the concentration, it may also act as a CB2 agonist or antagonist. It can potentially reverse THC’s effects by inhibiting its activity. THCV can be useful for treating nerve pain and reducing inflammation, two conditions associated with obesity.
The drug is known to be neuroprotective and may be effective in treating many neurological disorders. In recent studies, THCV has shown promise in treating PTSD and Alzheimer’s disease. It is also being studied as a treatment for osteoporosis, a common condition associated with poor bone density. Some people may even find it helpful for weight loss. While these applications are still in the experimental stage, there are many promising uses for THCV and various reasons why you should buy THCV.
Cannabigerol Acid
Cannabigerol acid (THCA) is a precursor to the cannabinoids THC and CBD. It is also known as CBGA. The two are chemically similar but have different functions in the human body. For example, THCV can suppress the tremors of Parkinson’s disease, ALS, and multiple sclerosis. It also reduces the frequency and severity of seizures.
Studies have indicated that THCV may act as an appetite suppressant, which could be helpful for obese people. It also improved the connectivity of brain areas associated with obesity. In addition, it inhibits the onset of junk-food cravings. Although more research is needed to prove this, it seems promising. A recent study published in the Journal of Pharmacology found that THCV reduced the swelling of mice.
CB1 Antagonist
The clinical efficacy of inverse agonists of the cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB1) has been growing for over a decade. Unfortunately, in 2008, a drug called Rimonabant has pulled off the market in Europe due to serious psychiatric side effects, and most large pharmaceutical companies abandoned efforts to develop CB1 inverse agonists. Since then, more studies have been performed, and more evidence is available to support the use of THCV.
A study of chronic THCV treatment in obese mice has demonstrated positive metabolic effects in overweight and obese mice. In addition, THCV reported initially as a CB1 neutral antagonist, was shown to produce an impact qualitatively different from AM251, the only known CB1 inverse agonist. The results of this study were the first to show the mechanism of action of THCV.
Insulin Resistance
The study reveals that THCV is capable of causing insulin resistance. It increases overall energy expenditure by increasing the phosphorylation of Akt in insulin-sensitive cells. However, it did not affect the activation of Akt in insulin-resistant cells. The results suggest that insulin resistance can be reversed by co-incubating the cells with THCV, AM251, or both. Further, THCV and AM251 may cause different effects on insulin receptor cell types.
In the study, insulin-sensitive cells were cultured in six-well plates. After 48 hours, they were either treated with vehicle or THCV. After this, they used serum-free media for the next two-hour period. At the end of the tolerance test, mice were reintroduced to food. The results were consistent with the findings obtained by other research. Insulin resistance is a symptom of diabetes, not a cause.
Anticonvulsant
THCV is an anticonvulsantsant with several properties. D9-THCV inhibits GABA release onto Purkinje cells at the network level, which supports its therapeutic potential in various hyperexcitability states. Moreover, D9-THCV shows a high affinity for CB1 receptors but lacks agonist action. In vitro studies revealed that D9-THCV can inhibit pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced seizures.
The effect of THCV on animal percentage ratios is inconsistent with the simple mode of the outbreak. Treatment with 70mg/kg of D9-THCV does not affect the mortality rate. However, with a higher dose, D9-THCV significantly reduces the number of animals that develop seizures. This finding also suggests that D9-THCV exhibits dose-dependent anticonvulsant activity in the PTZ model.
Appetite-Suppressant
As an appetite suppressant, THCV has been linked to various medical conditions. It is helpful in people with food-related disorders, such as Binge Eating disorders. It is not considered a long-term weight loss solution, so it is best to use it under your doctor’s direction.
THCV is similar to THC, a constituent of marijuana with a boiling point of 220 degrees Celsius. Because of its appetite-suppressing properties, it should be avoided by those suffering from a food-related addiction. However, it may benefit patients with diabetes, insulin resistance, or blood sugar regulation. It is still unknown whether THCV is a suitable treatment for these conditions.